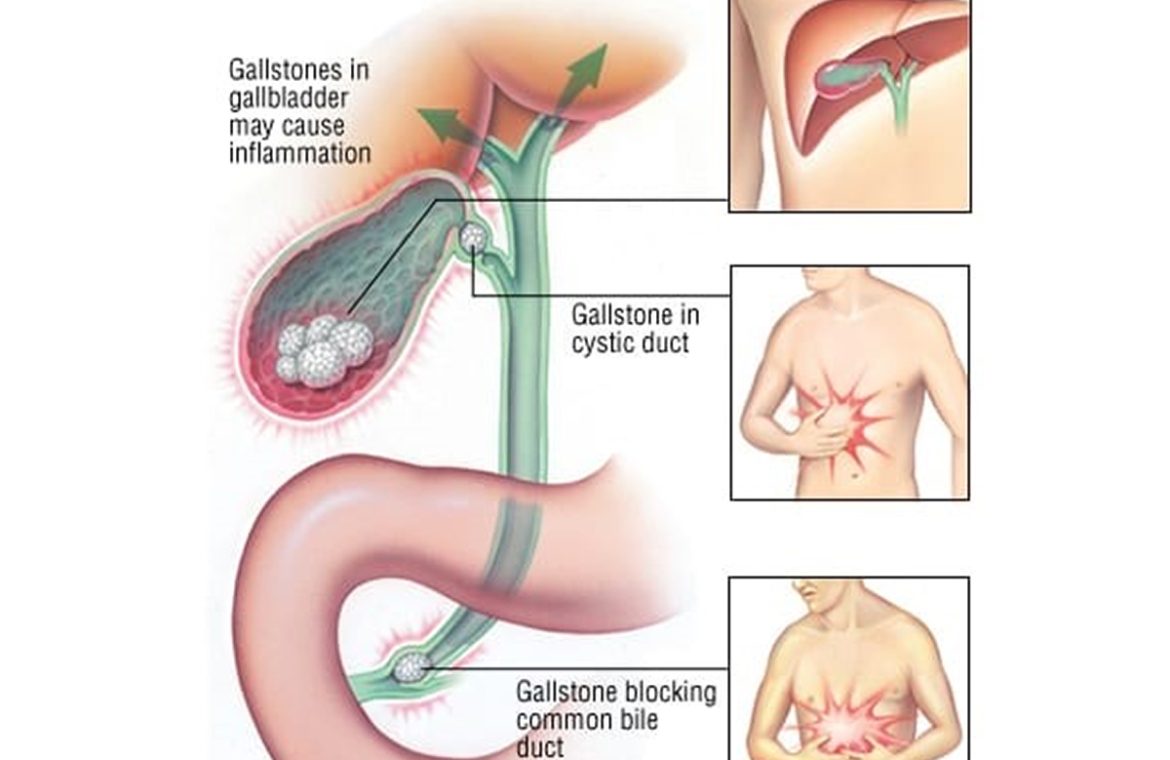
Gallstones/Cholelithiasis /Cholecystitis
Gallstones, medically known as cholelithiasis, are solid particles that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver. These stones can vary in size and can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe pain.
To know more about gallstones, contact Dr Vikram Ramamurthy, the GALLSTONE SPECIALIST IN BANGALORE. Dr. Vikram Ramamurthy is a highly accomplished and compassionate BEST GALL STONE SPECIALIST with an unwavering commitment to delivering exceptional patient care and surgical excellence. With extensive expertise in a wide range of surgical procedures, Dr. Vikram Ramamurthy brings a wealth of experience and proficiency to the operating room. Known for his meticulous approach and precise surgical techniques, Dr. Vikram Ramamurthy consistently ensures optimal patient outcomes and recovery. His dedication to staying at the forefront of medical advancements and his adeptness in leveraging cutting-edge technologies make him a trusted and sought-after practitioner in the field of general surgery. Dr. Vikram Ramamurthy’s exceptional patient-centric approach establishes him as a reliable and empathetic healthcare provider dedicated to fostering a culture of wellness and holistic patient well-being. He had carved a niche for giving the BEST GALL STONE TREATMENT in Bangalore with his experience and service.
Dr.Vikram Ramamurthy also specializes in advanced laparoscopic surgery for gastrointestinal problems like hernia, gallbladder stones, appendicitis, hepatobiliary and pancreatic diseases, colorectal diseases, piles, fissures, and fistulas in ano, with premium pre- and post-surgical care, making him one of the best gastrointestinal surgeons in Bangalore. He has general surgical problems like GERD, breast, thyroid diseases, varicose veins, diabetic wound, phimosis, lipoma, and sebaceous cyst.
In addition to his clinical work, Dr. Ramamurthy dedicates time to educating the next generation of surgeons. As a mentor and teacher, he instils the values of constant improvement and patient-centric care in his proteges.
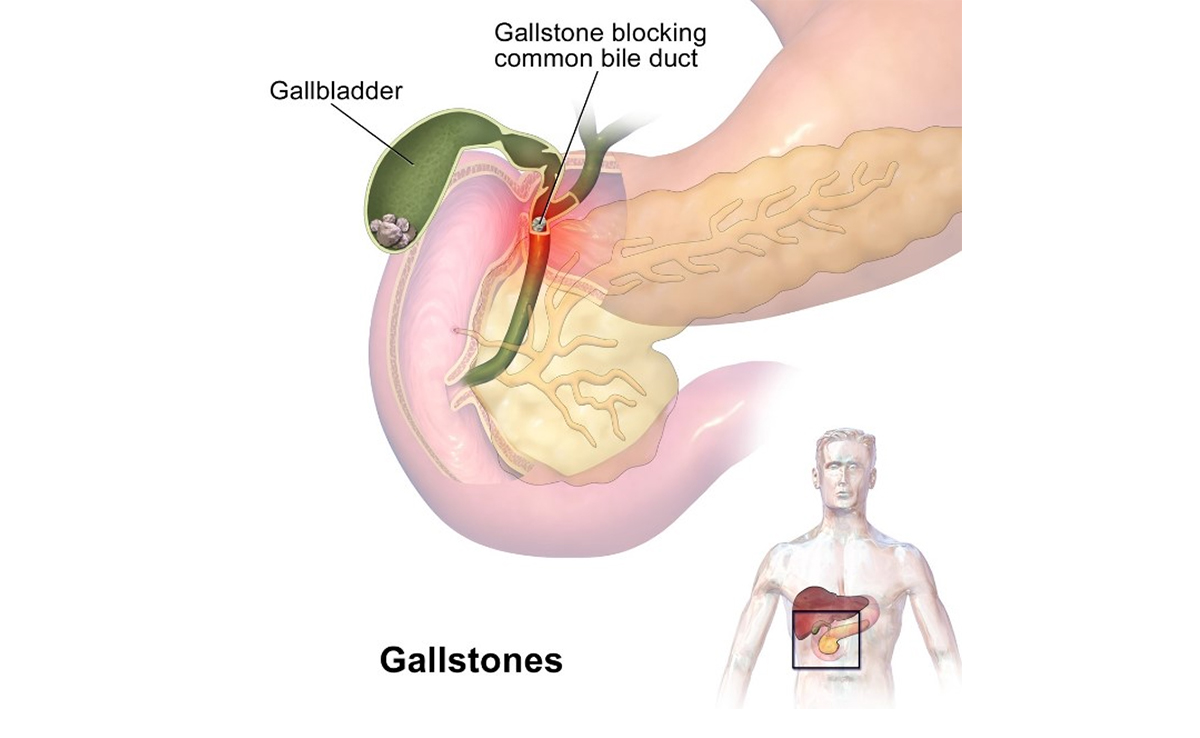
Causes
Gallstones are formed when the balance of substances that make up the bile, a digestive fluid produced by the liver, becomes disrupted. There are several factors that can contribute to the development of gallstones:
- Cholesterol Levels: The majority of gallstones are made of cholesterol. When there is an excess of cholesterol in bile, it can crystallize and form stones.
- Bilirubin Levels: Pigment stones can form when there is too much bilirubin in the bile. This can occur due to conditions like cirrhosis, haemolysis, or certain blood disorders.
- Gallbladder Motility: A sluggish gallbladder can lead to the stagnation of bile, which increases the risk of stone formation. Genetics: A family history of gallstones can increase your risk of developing them.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese is a significant risk factor for gallstones.
- Rapid Weight Loss: Losing weight too quickly, such as through crash dieting or bariatric surgery, can increase the risk of gallstones.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes during pregnancy can lead to the formation of gallstones.
- Certain Medical Conditions: Conditions like Crohn’s disease, diabetes, and metabolic syndrome can increase the risk of gallstones.

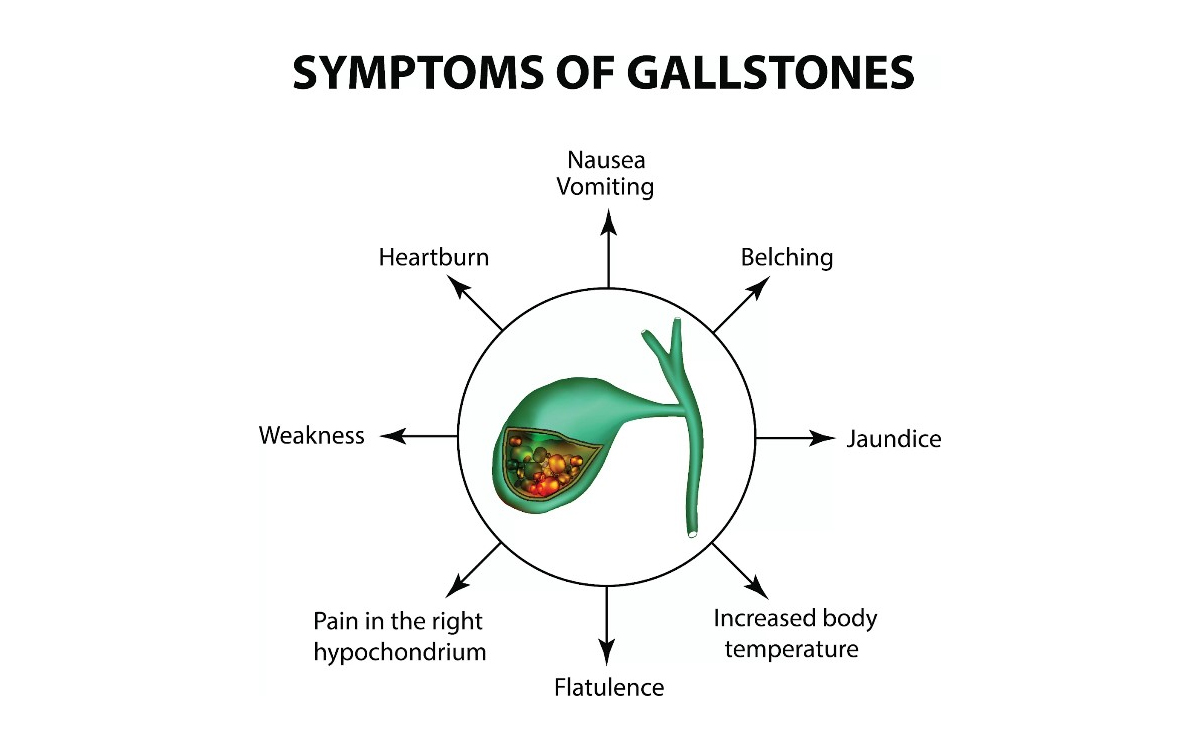
Symptoms
Gallstones don’t always cause symptoms. When they do, the symptoms can vary in intensity. Common symptoms of gallstones include:
- Biliary Colic: This is a sudden, intense pain in the upper right abdomen, typically triggered by fatty meals. The pain can radiate to the back and shoulder blades and may last for several hours.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Many people with gallstones experience nausea and may vomit during or after an episode of biliary colic.
- Jaundice: If a stone gets stuck in the bile duct, it can lead to jaundice, which causes yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes.
- Fever and Chills: In some cases, gallstones can lead to inflammation and infection in the gallbladder, causing fever and chills.
- Indigestion: Symptoms like bloating, gas, and burping can occur, especially after meals.
- Dark Urine and Light Stools: When bile flow is obstructed, urine may become darker, and stools may become lighter in color.
Diagnosis
If you suspect you have gallstones or experience symptoms, consult a healthcare professional. Diagnosis typically involves:
- Medical History: The doctor will ask about your symptoms and medical history.
- Physical Examination: A physical examination may reveal tenderness or swelling in the abdomen.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can help identify elevated bilirubin levels, a sign of gallbladder or bile duct problems.
- Imaging Studies: Various imaging tests are used to visualize the gallbladder and detect gallstones, including ultrasound, CT scans, and MRI.
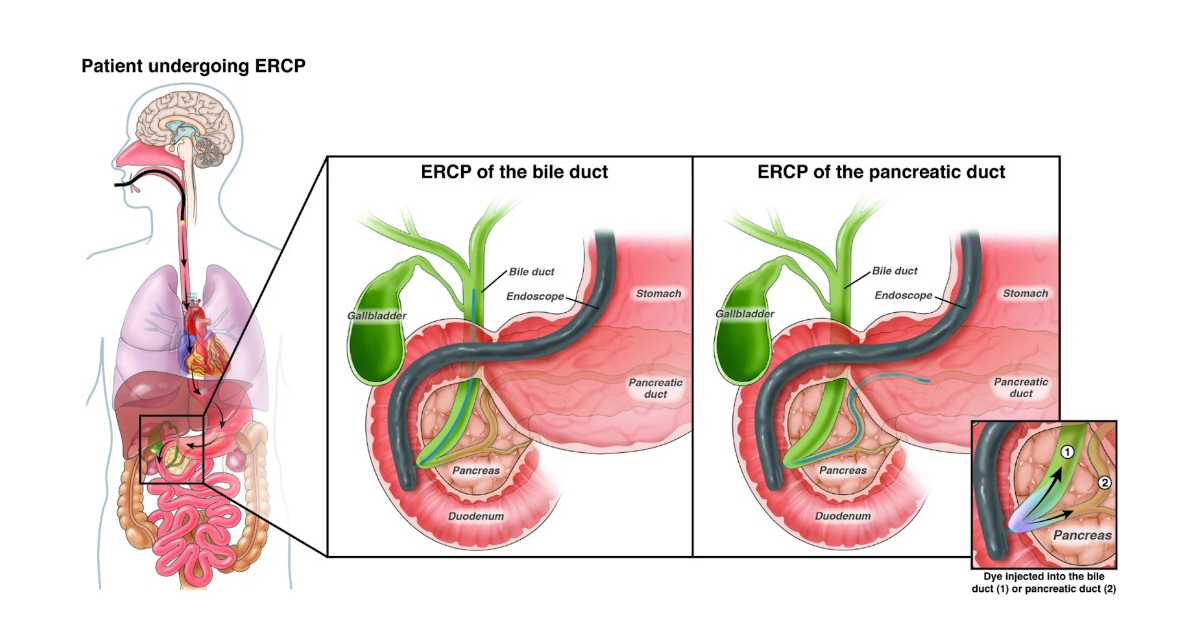
- Endoscopic Procedures: In some cases, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) or a magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) may be performed to obtain more detailed images of the gallbladder and bile ducts.
Diagnosis
The management of gallstones depends on their size, symptoms, and complications. Treatment options include:
- Watchful Waiting: If you have small, asymptomatic gallstones, your doctor may recommend watchful waiting. This means monitoring for any symptoms or complications but not actively treating the stones.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a low-fat diet and maintaining a healthy weight can help reduce the risk of gallstone formation.
- Medications: In some cases, medications like ursodeoxycholic acid may be prescribed to dissolve small cholesterol gallstones over time.
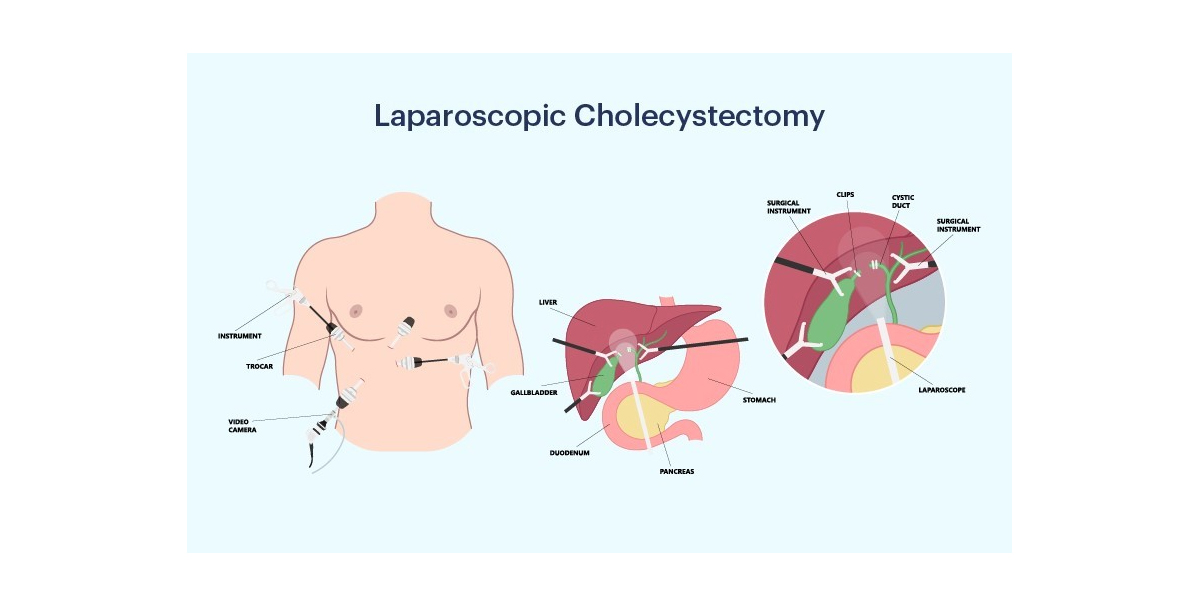
- Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy: This is the most common surgical procedure for gallstones. It involves the removal of the gallbladder, and it is usually done using minimally invasive techniques, resulting in a shorter recovery time.
- Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): In cases where gallstones have migrated to the bile duct, ERCP can be used to remove or break them up.
- Percutaneous Cholecystostomy: This procedure may be necessary if a patient is too ill for surgery. It involves draining the gallbladder through the skin.
- Open Cholecystectomy: In rare cases, an open surgery to remove the gallbladder may be necessary, particularly if there are complications.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of gallstones, consider the following preventive measures:
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Consume a diet low in saturated fats and cholesterol while emphasizing fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Gradual Weight Loss: If you need to lose weight, do so gradually to minimize the risk of gallstones forming during rapid weight loss.
- Stay Active: Regular physical activity can help prevent gallstones.
- Moderate Alcohol Intake: Excessive alcohol consumption can increase the risk of gallstones, so consume alcohol in moderation
- If you have gall stones or cholelithiasis or experience symptoms of gall stone, it is advisable to consult Dr. Vikram Ramamurthy for an accurate diagnosis and the best treatment option tailored to you. Book an appointment by calling:
- +918660296440
- +918431751624
- +919535958697